La importancia de la alelopatía en la obtención de nuevos cultivares
IMPORTANCIA DE LA ALELOPATÍA EN LA OBTENCIÓN DE NUEVAS VARIEDADES
Las recientes investigaciones sobre la alelopatía del arroz han avanzado la posibilidad de obtener cultivos alelopáticos de arroz por las siguientes razones:
- existe variación en la alelopatía de los cultivares de arroz;
- la alelopatía tiene una función importante bajo las condiciones de campo;
- la alelopatía en el arroz es efectiva sobre monocotiledóneas y dicotiledóneas;
- la identificación de los compuestos aleloquímicos del arroz ha hecho importantes progresos;
- han sido determinados los loci con características cuantitivas (QTL) correlacionados con la alelopatía (Olofsdotter, 200b).
Importancia ecológica
En todos los ecosistemas de arroz los herbicidas se han convertido en uno de los más importantes componentes de control de malezas. Existen dos razones para explicar el creciente uso de herbicidas, el primero de ellos es la adopción generalizada de variedades de alto rendimiento que ha creado incentivos económicos para que los agricultores reduzcan la infestación de las malezas; en segundo lugar se encuentra la disponibilidad de herbicidas a bajo costo con la consecuencia de que el costo del control de malezas por medio de los herbicidas en los arroces sembrados en húmedo es menos de una quinta parte del costo de una sola remoción manual de las malezas como ocurre en Iloilo, Filipinas (Moody, 1991). Situaciones similares existen en West Java, Indonesia, y el delta del Mekong, en Viet Nam (Pandy y Pingati, 1996).
- evolución de malezas resistentes (Valverde et al., 2000);
- efectos residuales sobre los cultivos sucesivos;
- desaparición de algunas malezas susceptibles como Brasenia schreberi y Sagittaria aginashi, lo que afecta la biodiversidad de las malezas (Itoh, 2000).
Importancia económica
El uso de cultivos alelopáticos puede reducir definitivamente el costo del control de malezas. Esta tecnología, que se basa en la tecnología de semillas es más fácilmente transferible a los sistemas de manejo con bajos insumos que prevalecen en la mayoría de los sistemas productores de arroz de Asia.
CARACTERES ALELOPÁTICOS
¿Qué son los caracteres alelopáticos? Son características morfológicas tales como rápida emergencia y vigor de las plántulas, rápida tasa de crecimiento que produce un denso dosel foliar, mayor altura de las plantas, mayor volumen de raíces y mayor duración del crecimiento, que aumentan la capacidad de los cultivares de arroz para competir con las malezas (Minotti y Sweet, 1981; Bekowitz, 1988). La altura de las plantas es a menudo descrita como uno de los factores más importantes en el total de la habilidad competitiva de un cultivo y cuenta por un porcentaje similar de la habilidad competitiva total (Gaudet y Keddy, 1988; Garrity et al., 1992). Sin embargo, no está claro si todas esas características están también relacionadas con la alelopatía.
Métodos de selección
Para seleccionar arroz con potencial alelopático se han sugerido varios métodos tales como: método «stairstep» (Bonner, 1950; Liu y Lovett, 1993); prueba de cultura hidropónica (Einhelig, 1985); técnica de relevo de semillas (Navarez y Olofsdotter, 1996); prueba del medio de agar-agar (Fujii, 1992; Wu et al., 1999); análisis de conglomerados usando HPLC -cromatografía líquida de alta presión (Mattice et al., 2001); método de extracto de agua (Kim et al., 1999; Ebana et al., 2001) y bioensayo de lámina de 24 huecos (Rimando et al., 1998). Cada uno de los métodos antes citados puede ser una útil herramienta para evaluar el potencial alelopático. Sin embargo, se debe tener en cuenta que las muestras o cultivares analizados por un cierto método pueden no siempre ser activos en el análisis de otro método. En términos de selección, el método de prueba directamente en el campo podría ser el mejor método para evaluar el potencial alelopático pero presenta dificultades cuando hay que trabajar con un gran número de materiales. Por lo tanto, es necesario identificar un bioensayo confiable y universal que genere una tendencia similar bajo diferentes condiciones. Para ello, es necesario un continuo desarrollo de sistemas de selección.
Diferente potencial alelopático
Análisis de los loci de características cuantitativas
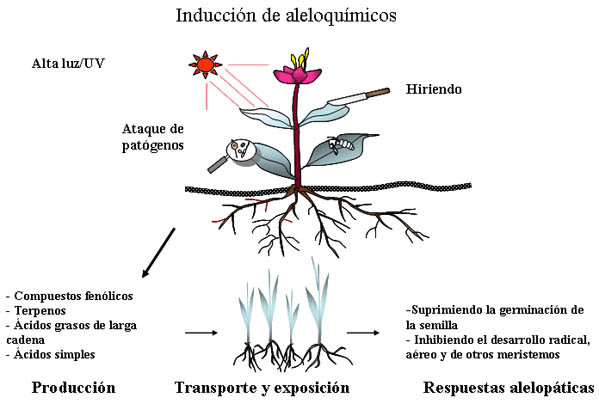
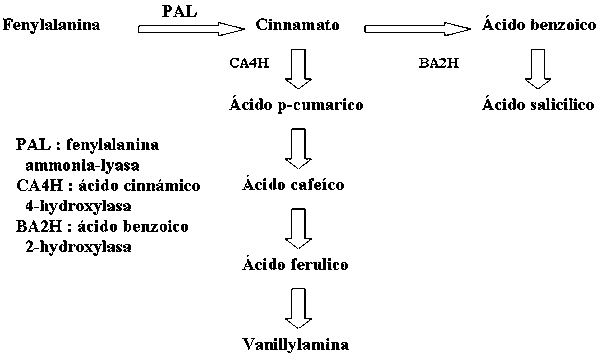
Hasta hace poco tiempo muchos estudios verificaron los mecanismos de un sistema de autodefensa, incluyendo la alelopatía en las plantas, especialmente referida al metabolismo de fenilpropanoides (Figura 2) e isoterpenoides (Figura 3). Las plantas responden al estrés ambiental por medio de una variedad de reacciones bioquímicas que pueden proporcionar protección contra los agentes causantes. El incremento de compuestos fenólicos y terpenoides alelopáticos bajo condiciones de estreses ambientales ha sido bien documentado. Por ejemplo, un fortalecimiento de la luz UV-B induce la acumulación de fenilpropanoides y flavonoides en diferentes especies tales como frijoles, perejil, papa, tomate, maíz, centeno, cebada y arroz (Hahlbrock y Scheel, 1989; Ballare et al., 1995; Tevini et al., 1991; Liu et al., 1995; Kim et al., 2000a).
Procesos para la síntesis de compuestos aleloquímicos
Todos los fenilpropanoides son derivados del ácido cinnámico el cual es formado a partir de la fenilalanina por acción catalítica de la fenilalanina amionioliasa (PAL), la enzima ramificada entre el metabolismo primario (proceso «shikimate») y secundario (fenilpropanoide) (Figura 2). Se sabe que muchos compuestos fenólicos no tienen solamente una capacidad fisiológica funcional sino también potencial alelopático para las plantas.
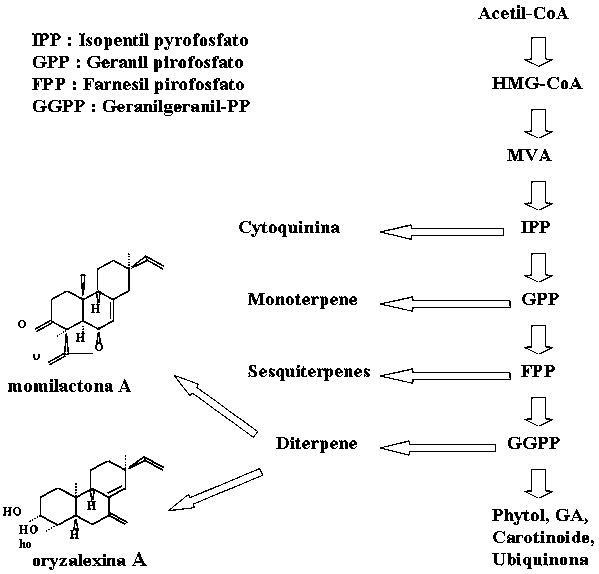
Compuestos aleloquímicos putativos
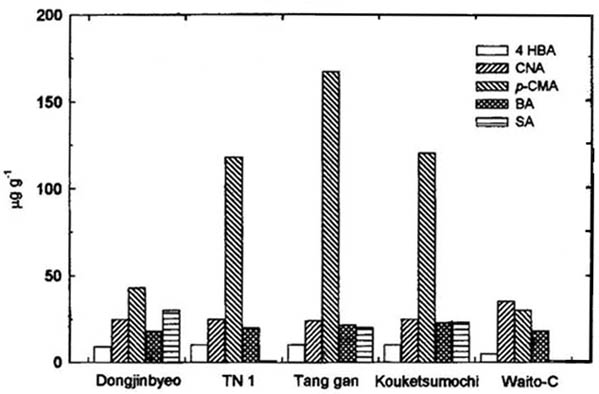
Existen una serie de estudios indicando que las comunes sustancias alelopáticas putativas encontradas en el arroz son compuestos fenólicos (Rice, 1987; Chou et al., 1991; Inderjit, 1996; Mattice et al., 1998; Blum, 1998). Kim et al. (2000b) identificaron varios compuestos por análisis GC/MS del cv. ‘Kouketsumochi’: compuestos potencialmente alelopáticos del arroz como esteroles, benzaldehidos, derivados del benzeno, ésteres de ácidos grasos de cadena larga, aldehidos, cetonas y aminas identificados en fracciones con actividad biológica. Varios compuestos alelopáticos del cultivar alelopático ‘Taichung Native 1’ han sido identificados por el método de aislación de bioensayo guiado (Rimando et al., 2001). Estos compuestos son ácido azelaico, ácido p-cumárico, 1H-indol-carboxyaldehido, 1H-indol-3-ácido carboxílico, 1H-indol-5-ácido carboxilíco y ácido 1,2-ácido benzenodicarboxílico bis (2-etilexilo) éster. Entre las sustancias alelopáticas identificadas, el ácido p-cumárico, un conocido compuesto aleloquímico, inhibió la germinación de plántulas de lechuga (Lactuca sativa L.) a una concentración de 1 mM pero fue activo contra Echinochloa spp. solamente a 3 Mm (Rimando et al., 2001). Kim et al. (2001b) informaron de una tendencia similar con el ácido p-cumárico que estuvo presente en arroces con potencial alelopático tales como ‘Kouketsumochi’, ‘Tang Gan’ y ‘Taichung Native 1’. Además, el contenido de este ácido se incrementó notablemente por irradiación UV (Figura 4).
ESTRATEGIAS PARA EL FITOMEJORAMIENTO DE CULTIVOS ALELOPÁTICOS
Los tres enfoques utilizados para crear cultivares alelopáticos son: i) el método tradicional de fitomejoramiento; ii) la incorporación de propiedades alelopáticas al arroz híbrido y iii) la ingeniería genética. Desde el punto de vista del fitomejoramiento, la distinción entre alelopatía y competencia es algo difícil de identificar en el campo del agricultor dado que el fenómeno realmente importante es la interferencia (Courtois y Olofsdotter, 1998). Al respecto, el mejor camino podría ser la obtención de cultivares alelopáticos con alta competitividad. Si efectivamente se pudieran obtener cultivares alelopáticos esta sería una importante contribución para los agricultores en los países productores de arroz.
Fitomejoramiento tradicional
Si están involucrados un alto número de QTL con efecto limitado, el método tradicional de fitomejoramiento puede ser una alternativa razonable (Courtois y Olofsdotter, 1998). El principio del fitomejoramiento tradicional para los estudios genéticos es simple. Dos líneas parentales con comportamiento contrastante son cruzadas y las líneas endocriadas recombinadas (RIL) son derivadas por medio del método de la descendencia de una sola semilla (SSD).
Arroz híbrido con alelopatía
El arroz híbrido de tres líneas producido en China es un buen competidor en razón de su rápido y profuso crecimiento vegetativo, en comparación con las líneas endocriadas. Sería útil que pudieran ser introducidos caracteres alelopáticos en la línea restauradora de la producción del arroz híbrido de tres líneas. Lin et al. (2000) intentaron la retrocurza y la autofecundación simultáneas para desarrollar arroz híbrido con actividad alelopática y su contraparte arroz híbrido isogénico con efecto no alelopático sobre las malezas. Tres líneas de arroz, ‘Kouketsumochi’, ‘Rexmont’ e ‘IR24’ fueron usadas como donantes de genes de alelopatía, de no alelopatía y restauradores, respectivamente. La retrocruza fue usada para desarrollar las líneas restauradoras con actividad alelopática y su línea isogénica con genes no alelopáticos. Las líneas restauradoras seleccionadas fueron cruzadas con líneas con citoplasma estéril (línea A) actualmente usadas para probar la tasa de cruzamiento (Figura 5); también se ilustra un esquema de como desarrollar arroz híbrido con potencial alelopático.
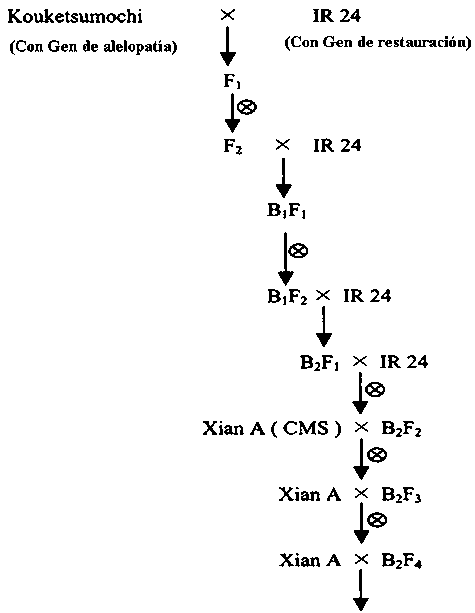
 =autofecundación
=autofecundaciónEnfoque molecular
Se han sugerido dos métodos para crear más cultivos alelopáticos: (1) la regulación de la expresión de los genes relacionada con la biosíntesis aleloquímica y, (2) la inserción de genes para producir compuestos aleloquímicos que no se encuentran en el cultivo (Duke et al., 2001). La mayor parte de la información actualmente disponible sobre la ingeniería de los compuestos aleloquímicos proviene de los esfuerzos de la sobreproducción de metabolitos secundarios valiosos en las plantas (Canel 1999). En relación con el enfoque molecular una referencia interesante ha sido publicada por Gressel (2002).
Regulación de la expresión de un gen relacionada con los compuestos aleloquímicos
Para regular la expresión de un gen, el primer requerimiento es identificar el compuesto o los compuestos aleloquímicos objetivo a fin de determinar las enzimas y los genes que los codifican; de esta manera un promotor específico puede ser inserido en las plantas cultivadas para fortalecer la producción de compuestos aleloquímicos.
Este enfoque emplea la alteración existente de los procesos bioquímicos por medio de la inserción de transgenes para producir nuevos compuestos aleloquímicos. Parece ser un enfoque difícil de emplear pero, sin embargo, es uno de los enfoques moleculares promisorios a ser desarrollados en el futuro cercano. Al respecto Duke et al. (2001) presentan una buena revisión y un libro de referencias sobre biología molecular del control de malezas ha sido recientemente publicado por Gressel (2002).
El mejoramiento del potencial alelopático de las variedades cultivadas tendrá un gran impacto sobre los sistemas de producción agrícola, tanto en aquellos sistemas de bajos insumos como en los de altos insumos. Es poco probable que la alelopatía por si sola puede reemplazar totalmente a otras prácticas de control de malezas ya que su efectividad es influenciada por muchos factores. Sin embargo, una reducción del uso de los herbicidas será un beneficio para los agricultores y también reducirá el impacto en el ambiente.
Back, K., He, S., Kim, K. U. y Shin, D. H. 1998. Cloning and bacterial expression of sesquiterpene cyclase, a key branch point enzyme for the synthesis of sesquiterpenois phytoalexin capsidiol in UV-challenged leaves of Capsicum annuum. Plant Cell. Physiolol. 39 (9): 899-904.
Ballare, C. L., Barnes, P. W. y Flint, S. D. 1995. Inhibition of hypocotyls elongation by ultraviolet-B radiation in de-etiolating tomato seedlings. I. The photoreceptor. Physiol. Plant 93: 584-592.
Banthorpe, D. V. 1991. Terpenoids classification of terpenoids and general procedures for their characterization. En: Terpenoids of Methods in Plant Biochemistry, Vol.7. Academic Press, London, pp.141.
Berkowitz, A.R. 1988. Competition for resources in weed-crop mixtures. En: Altiera, M.A and Liebman, M. eds Weed management in agrosystems: ecological approaches. Boca Ratón, Florida, CRC Press. Pp. 89-119.
Blum, U. 1998. Effect of microbial utilization of phenolic acid and their phenolic acid breakdown products on allelopathic interactions. J. Chem. Ecol. 24:685-708.
Bonner, J. 1950. The role of toxic substances in the interactons of higher plants. The Botanical Review 16:51 51-65.
Canel, C. 1999. From genes to phytochemicals: the genomics approach to the characterization and utilization of plant secondary metabolism. Acta Hortic. 500: 51-57.
Christensen, S. 1993. Weed supression in cereal varieties. Min. Agric. Statens Planeavlsforsog. Denmark. N° 1. P 104. (Tesis Ph. D.).
Chou, C. H., Chang, F. J. y Oka, H. I. 1991. Allelopathic potential of wild rice Oryza perennis. Taiwania 36 (3) 201-210.
Courtois, B. y Olofsdotter, M. 1998. Incorporating the alleolopathy trait in upland rice breeding programs. En: Olofsdotter, M. ed. Allelopathy in Rice. Manila, Filipinas: Int. Rice Research Institute. pp. 57-68.
Dilday, R. H., Nastasi, P., Lin, J. y Smith, R. J., Jr. 1991. Allelopathic activity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) against ducksalad (Heteranthera limosa [Sw.] Willd.) En: D. Hanson, M. J. Schaffer. D. A. Ball and C. V. Cole eds.Symposium Proc. on Sustainable Agriculture for the Great Plains. USDA, ARS-89. pp. 193-201.
Dilday, R. H., Yan, W. G., Moldenhauer, K. A. K. y Gravois, K. A. 1998. Allelophatic activity in rice for controlling major aquatic weeds. En: Olofsdotter, M., ed Allelopathy in rice. Manila, Filipinas: Int. Rice Research Institute. pp. 7-26.
Duke, S. O., Scheffler, B. E., Dayan, F. E., Weston, L. A. y Ota, E. 2001. Strategies for using transgenes to produce allelopathic crops. Weed Tech. 15: 826-834.
Ebana, K., Yan, W., Dilday, R. H., Namai, H. y Okuno, K. 2001. Variation in the allelopathic effect of rice with water soluble extracts. Agronomy J. 93: 12-16
Einhehelig, F. A., Leather, G. R. y Hobbs, L. 1985. Use of Lemma minor L. as a bioassay in allelopathy. J. Chemical Ecology 11(1): 65-72.
Fay, P. K. y Duke, W. B. 1977. An assessment of allelopathic potential in Avena germoplasm. Weed Sci. 25: 224-228.
Fujii, Y. 1992. The potential biological control of paddy weeds with allelopathy: allelopathic effect of some rice varieties En: Int. Symposium on Biological Control and Integrated Management of Paddy and Aquatic Weeds in Asia. Tsukuba, Japón. National Agricultural Research Center. pp. 305-320.
Garrity, D. P., Movillon, M. y Moody, K. 1992. Differential weed suppression ability in upland rice cultivars. Agron. J. 84: 586-591.
Gaudet, C. L. y Keddy, P. A. 1988. A comparative approach to predicting competitive ability from plant traits. Nature 334: 242-243.
Gershenzon, J. y Croteau, R. 1993. Terpenoid biosynthesis: the basic pathway and formation of monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes and diterpenes. En: T. S. Moore., ed. Lipid metabolism in plants. CRC Press, Boca Ratón, Florida, Estados Unidos de América. pp 340-388.
Gressel, J. 2002. Molecular Biology of Weed Control. Taylor and Francis Publishers, London.
Hahlbrock, K y Scheel, D. 1989. Physiology and molecular biology of phenylpropanoid metaboism. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 40: 347-369.
Hill, J. E., Roberts, S. R., Scardaci, S. C. y Williams, J. F. 1997. Rice herbicides and water qualitu. A California success story in government and industrial coordination. Proc. of 16th Asian Pacific Weed Society Conference (Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia). Asian-Pacific Weed Science Society, Kuala Lumpur, pp 388-392.
Inderjit. 1996. Plant phenolics in allelopathy. Bot. Rev. 62: 186-202.
Itoh, K. 2000. Importance of biodiversity of aquatic plants in agro-ecosystem for rice production. En: Abstracts of the Int. Symposium on Weed Biodiversity (National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 28-30 November, 2000). Weed Science Society of the Republic of China and National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaoshing, p. 10.
Jensen, L. B., Coourtois, B., Shen, L., Li., Z., Olofsdotter, M. y Mauleon, R. P. 2001. Location genes controlling rice allelopathic effects against barnyardgrass in upland rice. Agron. J. 93: 21-26.
Khush, G., S. 1966. Genetic improvement of rice for weed management. En: Naylor, R., ed Herbicides in Asian rice: transitions in weed management. Palo Alto (California): Institute for Int. Studies, Stanford University and Manila (Filipines) Int. Rice Research Institute. pp 201-207.
Kim, K. U. y Shin, D. H. 1998. Rice allelopathy research in Korea. En: M. Olofsdotter, ed. Proc. of the Workshop on Allelopathy in Rice, 25-27 November 1996. Manila (Philippines): Int. Rice Research Institute. pp. 39-44.
Kim, K. U., Shin, D. H., Kim, H. Y. Lee, I. J. y Olofsdotter, M. 1999. Evaluation of allelopathic potential in rice germoplasm. Korean J. of Weed Sci. 9(2): 1-9.
Kim, K. U. 2000. Weed management implication and trends of direct seeding in Asia. Third Int. Weed Science Congress (Foz do Iguassu, Brazil, 6-11 June 2000). Int. Weed Science Society, Corvallis, Maniscript N° 508, pp 1-10.
Kim, H. Y., Shin, H. Y., Sohn, D. S., Lee, I. J., Kim, K. U., Lee, S. C., Jeong, H. J. y Cho, M. S. 2000a. Enzyme activities and compounds related to self-defense in UV-challenged leaves of rice. Korean J. Crop. Sci. 46 (1): 22-28.
Kim, K. W., Kim, K. U., Shin, D. H., Lee, I. J., Kim, H. Y., Koh, J. C. y Nam, S. H. 2000b. Searching for allelochemicals from allelopathic rice cultivar ‘Kouketsumochi’. Korean J. of Weed Sci. 20 (3): 197-207.
Leather, G. R. 1983. Sunflowers (Helianthus annuus) are allelopathic to weeds. Weed Sci. 31: 37-42.
Lin, W., Kim, K. U., Liaang, K. y Guo, Y. 2000.Hybrid rice with allelopathy. En: K. U. Kim and Shin, D. H. eds. Rice allelopathy. Proc. of the Int. Workshop in Rice Allelopathy (Kyungpook, National University, Taegu, Korea, 17-19 August 2000). Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology, Kyungpook National University, Taegu, pp. 49-56.
Liu, D. L. y Lovett, J. V. 1993. Boplogically active secondary metabolites of barley. 1. Developing techniques and accessing allelopathy in barley. J. of Chemical Ecology 19 (10): 2217-2230.
Liu, L., Gitz, D. C. y McClure, M. W. 1995. Effect of UV-B on flavonoids, ferulic acid, growth and pshotosynthesis in barley primary leaves. Physiol. Plant 93: 725-733.
Lovett, J. V. y Hoult, A. H. C. 1995. Allelopathy and self-defense in barley. An. Chem. Soc. Symp. Ser. 582: 170-183.
Mattice, J. D., Lavy, T., Skulma, B. W. y Dilday, R. H. 1998. Searching for allelochemicals in rice that control ducksalad. En: Olofsdotter., ed. Allelopathy in rice. Proc. Workshop on Allelopathy in Rice. Manila, Philippines, 25-27 Nov. 1996. IRRI, Manila, Filipinas. pp. 81-98.
Mattice, J. D., Dilday, R. H., Gbur, E. E. y Skulman, B. W. 2001. Barnayardgrass growth inhibition with rice usinf high-performance liquid chromathography to identify rice accession activity. Agron. J. 93: 8-11.
Minotti, P. L. y Sweet, R. D. 1981. Role of crop competition in limiting losses from weeds. En: D. Pimental ed. Handbook of pest management in agriculture. Vol. II. Boca Ratón, Florida, Estados Unidos de América. CRC Press. pp. 351-367.
Moody, K. 1991. Weed management in rice. En: Handbook of Pest Management in Agriculture 2nd edition. Pimental, D. ed. CRC Press, Boca Ratón, Florida, Estados Unidos de América. pp. 301-328.
Moreno-González, J. y Cubero, J. I. 1993. Selection strategies and choice of breeding methods. En: Hayward, M. D., ed. Plant Breeding. Chapman and Hall, pp. 296-297.
Navarez, D. y Olofsdotter, M. 1996. Relay seeding procedure as screening method in allelopathy research. Proc. 2nd Int. Weed Control Conf. 4: 285-290.
Nimbal, C. I., Yerkes, C. N., Weston, L. A. y Weller, S. C. 1996. Herbicidal activity and site of action of the natural product sorgoleone. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 54: 73-83.
Olofsdotter, M., Navarez, D., Rebulanan, M. y Streibig, J. C. 1999. Weed suppressing rice cultivars - does allelopathy play a role? Weed Res. 39: 441-454.
Olofsdotter, M. 2001a. Getting closer to breeding for competitive ability and the role of allelopathy -an example from rice (Oryza sativa). Weed Tech. 15: 798-806.
Olofsdotter, M. 2001b. Rice -a step toward use of allelopathy. Agron. J. 93: 3-8.
Olofsdotter, M. Rebulanan, M., Madrid, A, Dali, W., Navarez, D. y Olk, D. C. 2001. Why phenolic acids are unlikely allelochemicals in rice?. J. Chem. Ecol. (en prensa).
Pandy, S. y Pingali, P. I. 1996. Economic aspects of weed management. En: Auld, B. A. and Kim, K. U. eds. Weed management in rice. FAO Plant Production and Protection Paper 139. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. pp. 55-73.
Patrick, A. Q., Toussoun, T. A. y Snyder, A. 1963. Phytotoxic substances in arable soils associated with decomposition of plant residues. Phytopathology 53: 152-161.
Putnam, A. R. y Duke, W. B. 1974. Biological suppression of weeds: evidence for allelopathy in accessions of cucumber. Science 185: 370-372.
Richardson, D. R. y William, G. B. 1988. Allelopathic effects os shrubs of the sand pine scrub on pines and grasses of sandhills. Forest Science 34: 592-605.
Rice, E. L. 1987. Allelopathy: an overview. Allelochenicals: role in agriculture and forestry. En: American Chemical Society, Symposium Series N° 330. pp. 8-22.
Rimando, A. M., Dayan, F. E., Czarnota, M. A., Weston, L. A. y Duke, S. O. 1998. A new photosystem. II. Electron transfer inhibitor from Sorghum bicolor, J. Nat. Prod. 61: 927-930.
Rimando, A. M., Olofsdotter, M., Dayan, F. E. y Duke, S. O. 2001. Searching for rice allelochemicals: an example of bioassay-guided isolation. Agron. J. 93: 16-20.
Shin, D. H., Kim, K. U., Sohn, D. S., Kang, S. U., Kim, H. Y., Lee, I. J. y Kim, M. Y. 2000. Regulation of gene expression related to allelopathy. En: Kim, K. U. y Shin, D. H., eds. Proc. of the Int. Workshop in Rice Allelopathy (Kyungpook National University, Taegu, Korea, 17-19 August 2000). Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology, Kyungpook National University, Taegu. pp. 109-124.
Tanaka, F., Ono, S. y Hayasaka, T. 1990. Identification and evaluation of toxicity of rice root elongation inhibitors in flooded soil with added wheat straw. Soil. Sci. Plant. Nutr. 36: 97-103.
Tevini, M., Braun, J. y Fieser, G. 1991. The protective function of epidermal layer of rye seedlings against ultraviolet-B radiation. Photochem. and Photobiol. 53: 329-333.
Valverde, B. E., Riches, C. R. y Caseley, J. C. 2000. Prevention and management of herbicide resistant weeds in rice. Published by Graphos, S. A., Cartago, Costa Rica. pp. 25-30.
Wu, H., Pratley, H., Lemerle, D. y Haig, T. 1999. Crop cultivars with allelopathic capability. Weed Res. 39: 171-180








