Efecto del control de garrapata en ganancia de peso en vaquillas
Efecto del control estratégico de la garrapata común del bovino Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus sobre la ganancia de peso en vaquillas Braford en el noreste de Argentina.
El objetivo de este trabajo fue analizar el impacto del control estratégico de Rhipicephalus microplus sobre la ganancia de peso de vaquillas Braford en el noreste de Argentina. Se realizaron dos experimentos con un diseño similar en localidades de Corrientes (Colonia Tabay) y Chaco (Colonia Benítez). Los distintos grupos de vaquillas fueron sujetos a esquemas de control estratégico que consistieron en la aplicación de tres o cuatro productos garrapaticidas entre agosto y diciembre, y se compararon el número de garrapatas y la ganancia diaria de peso (GDP) entre estos y un grupo testigo que no recibió garrapaticidas. En Colonia Tabay, en los dos grupos tratados con esquemas de control estratégico la GDP fue significativamente mayor que en el grupo testigo con mayor nivel de infestación con garrapatas. El grupo sujeto a control estratégico en Colonia Benítez también tuvo una GDP significativamente mayor que el grupo testigo. Las diferencias en las GDP entre los grupos de animales sujetos a control estratégico y aquellos mantenidos como grupos testigo fluctuó entre 0.09 y 0.149 kg/día. Para el período evaluado en este trabajo (nueve meses), la aplicación del control estratégico contra R. microplus implicó una ganancia diferencial con respecto a los grupos sin tratamientos de 29 y 42 kg en promedio en las vaquillas de Colonia Tabay y de 25 kg en aquellas de Colonia Benítez. De los resultados se desprende que la aplicación de esquemas de tratamientos estratégicos para controlar la infestación con R. microplus en el noreste de Argentina contribuye a disminuir significativamente la abundancia de garrapatas y posibilita obtener mejores ganancias de peso vivo en bovinos en crecimiento al prevenir altos niveles de parasitación en los animales.
Palabras clave: garrapatas, control, bovinos, ganancia de peso, Argentina.
INTRODUCCIÓN
MATERIALES Y MÉTODOS
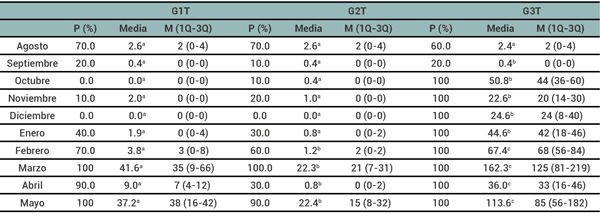
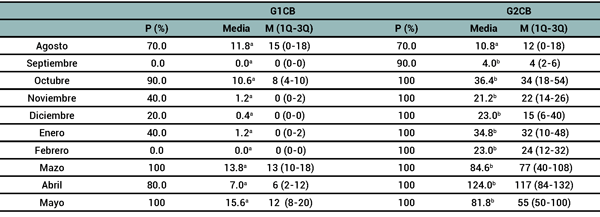
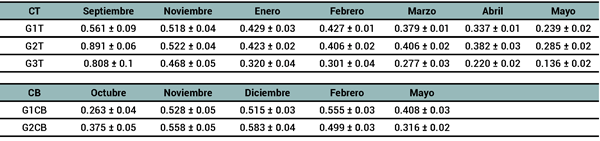
RESULTADOS
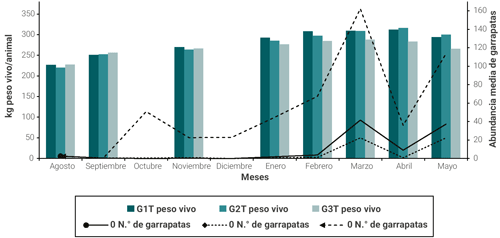
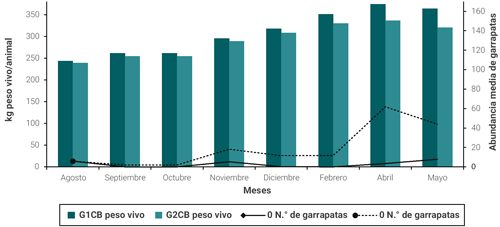
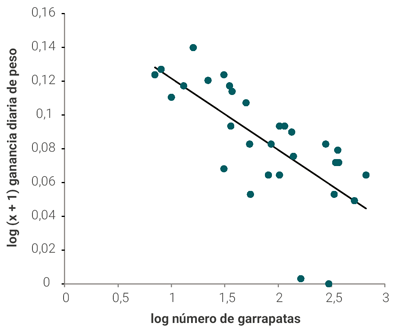
DISCUSIÓN
CONCLUSIÓN
AGRADECIMIENTOS
BARNETT, S.F. 1961. The control of ticks on livestock. Agriculture Studies N.o 54, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Roma,115 p.
BUSH, A.O.; LAFFERTY, K.D.; LOTZ, J.M.; SHOSTAK, A.W. 1997. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. Revisited. J. Parasitol. 83: 575-583.
CUTULLÉ, C.; LOVIS, L.; D´AGOSTINO, B.I.; BALBIANI, G.G.; MORICI, G.; CITRONI, D.; REGGI, J.; CARACOSTANTOGOLO, J.L. 2013. In vitro diagnosis of the first case of amitraz resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus in Santo Tomé (Corrientes), Argentina. Vet. Parasitol. 192: 296-300.
ESTRADA-PEÑA, A.; VENZAL, J.M.; NAVA, S.; MANGOLD, A.J.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A.; LABRUNA, M.B.; DE LA FUENTE, J. 2012. Reinstatement of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) australis (Acari: Ixodidae) with redescription of the adult and larval stages. J. Med. Entomol. 49: 794-802.
GEE, R.W.; BAINBRIDGE, M.H.; HASLAN, J.Y. 1971. The effect of cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) on beef production in the Northern territory. Aust. Vet. J. 47: 257-261.
GUGLIELMONE, A.A. 1992. The level of infestation with the vector of cattle babesiosis in Argentina. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 87: 133-137.
GUGLIELMONE, A.A. 1995. Epidemiology of babesiosis and anaplasmosis in South and Central America. Vet. Parasitol. 57: 109-119.
GUGLIELMONE, A.A.; NAVA, S. 2013. Epidemiología y control de las garrapatas de los bovinos en la Argentina. En: NARI, A.; FIEL, C. (eds.). Enfermedades parasitarias con importancia clínica y productiva en rumiantes: fundamentos epidemiológicos para su diagnóstico y control. Editorial Hemisferio Sur, Buenos Aires. 441-456 pp.
GUGLIELMONE, A.A.; MANGOLD, A.J.; CASTELLI, M.; SUÁREZ, V.H.; AGUIRRE, D.H.; ALCARAZ, E.; CAFRUNE, M.M.; CETRÁ, B.; FADER, O.W.; LUCIANI, C.A.; MEDUS, P.D.; NAVA, S. 2006. Toxicidad in vitro de la cipermetrina para Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Can.) y del diazinón para Haematobia irritans (L.) en la Argentina. Rev. Inv. Agropec. 35: 31-41.
HALL, J.B. 2013. Nutritional development and the target weight debate. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 29: 537-554.
HOLROYD, R.G.; DUNSTER, P.J. 1978. The effect of the cattle tick on growth rates and reproductive rates of Bos indicus cross heifers in north Queensland. Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. 12, 227.
IVANCOVICH, J.C. 1989. Infestación natural por garrapatas Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) en bovinos. Bol. Cent. Reg. Chaco-Formosa Inst. Nac. Tecnol. Agropec. 101: 6-21. JONGEJAN, F.; UILENBERG, G. 2004. The global importance of ticks. Parasitology. 129: 1-12.
JONSSON, N.N. 2006. The productivity effects of cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) infestation on cattle, with particular reference to Bos indicus cattle and their crosses. Vet. Parasitol. 137: 1-10.
JOHNSTON, L.A.Y.; HAYDOCK, K.P.; LEATCH, G. 1981. The effect of two systems of cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) control on tick populations, transmission of Babesia spp. and Anaplasma spp. and production of Brahman crossbred cattle in the dry tropics. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb. 21: 256-267.
MELLOR, W.; O´ROURKE, P.K.O.; WATERS, K.S. 1983. Tick infestations and their effect on growth of Bos indicus x Bos Taurus cattle in the wet tropcis. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb. 23, 348-353.
MANGOLD, A.J.; MASTROPAOLO, M. 2013. Epidemiología y control de hemoparásitos (Babesia y Anaplasma) en Argentina. En: NARI, A.; FIEL, C. (eds.). Enfermedades parasitarias con importancia clínica y productiva en rumiantes: fundamentos epidemiológicos para su diagnóstico y control. Editorial Hemisferio Sur, Buenos Aires, 639-655 pp.
MANGOLD, A.J.; CASTELLI, M.E.; NAVA, S.; AGUIRRE, D.H.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A. 2004. Poblaciones de la garrapata Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus resistentes a los piretroides en Córdoba y Salta, Argentina. Revista FAVE (Ciencias Veterinarias) 3, 55-59.
MOREL, N.; SIGNORINI, M.L.; MANGOLD, A.J.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A.; NAVA, S. 2017. Strategic control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus infestation on beef cattle grazed in Panicum maximum grasses in a subtropical semi-arid region of Argentina. Prev. Vet. Med. 144: 179-183.
NAVA, S.; MANGOLD, A.J.; CANEVARI, J.T.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A. 2015. Strategic applications of long-acting acaricides against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in northwestern Argentina, with an analysis of tick distribution among cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 208, 225-230.
NAVA, S.; MOREL, N.; MANGOLD, A.J.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A. 2018. Un caso de resistencia de Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) al fipronil detectado en pruebas de campo en el este de Santiago del Estero, Argentina. Revista FAVE (Ciencias Veterinarias) 17: 1-5.
NAVA, S.; TOFFALETTI, J.; MOREL, N.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A.; MANGOLD, A.J. 2019. Testing the efficacy of winter-spring strategic control against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus infestations on cattle in an area with highly favorable ecological conditions for the tick in northeastern Argentina. Med. Vet. Entomol. 33: 312-316.
NAVA, S.; ROSSNER, M.V.; TORRENTS, J.; MOREL, N.; MARTÍNEZ, N.C.; MANGOLD, A.J.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A. 2020. Management strategies to minimize the use of synthetic chemical acaricides in the control of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Canestrini, 1888) in an area highly favourable for its development in Argentina. Med. Vet. Entomol. 34: 264-278.
O´KELLY, J.C.; SEEBECK, R.M.; SPRINGELL, P.H. 1971. Alterations in host metabolism by the specific and anorectic effects of the cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) ii. Chnages in blood composition. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 24: 381-389.
O´ROURKE, P.K. 1982. Repetability of tick counts and the relationship between tick count and liveweight change in growing Bos indicus x Bos Taurus cattle. Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. 14: 305-308.
PATTERSON, D.J.; OERRY, R.C.; KIRACOFE, G.H.; BELLOWS, R.A.; STAIGMILLER, R.B.; CORAH, L.R. 1992. Management considerations in heifer development and puberty. J. Anim. Sci. 70: 4018-4035.
RECK, J.; MARKS, F.S.; RODRIGUES, R.O.; SOUZA, U.A.; WEBSTER, A.; LEITE, R.C.; GONZALEZ, J.C.; KLAFKE, G.M.; MARTINS, J.R. 2014. Does Rhipicephalus microplus tick infestation increase the risk for myiasis caused by Conchliomyia hominivorax in cattle? Prev. Vet. Med. 113: 59-62.
ROBERTS, F.; O ́SULLIVAN, P. 1949. Methods for egg counts and larval culture for strongyles infesting gastrointestinal tract of cattle. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1: 99-102.
ROUVIER, A.M.; YAÑEZ, E.A. 2017. Efecto de la ganancia de peso invernal sobre el desarrollo genital de vaquillas a los 18 meses. Rev. Vet. 28: 93-98.
SCHOLTZ, M.M.; SPICKETT, A.M.; LOMBARD, P.E.; ENSLIN, C.B. 1991. The effect of tick infestation on the productivity of cows of three breeds of cattle. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 58: 71-74.
SEEBECK, R.M.; SPRINGELL, P.H.; O´KELLY, J.C. 1971. Alterations in host metabolism by the specific and anorectic effects of the cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) i. Food intake and body weight growth. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 24: 373-380.
SPRINGELL, P.H.; O´KELLY, J.C.; SEEBECK, R.M. 1971. Alterations in host metabolism by the specific and anorectic effects of the cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) iii. Metabolic implications of blodd volume, body water, and carcass composition changes. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 24: 1033-1045.
SUTHERST, R.W.; MAYWALD, G.F.; KERR, J.D.; STEGEMAN, D.A. 1983. The effect of cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) on the growth of Bos indicus x B. taurus steers. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 34: 317-327.
SPÄTH, E.J.A.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A.; SIGNORINI, A.R.; MANGOLD, A.J. 1994. Estimación de las pérdidas económicas directas producidas por la garrapata Boophilus microplus y las enfermedades asociadas en la Argentina (1.a parte). Therios 23: 341-360.
TORRENTS, J.; SARLI, M.; ROSSNER, M.V.; TOFFALETTI, J.R.; MOREL, N.; MARTINEZ, N.C.; WEBSTER, A.; MANGOLD, A.J.; GUGLIELMONE, A.A.; NAVA, S. 2020a. Resistance of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus to ivermectin in Argentina. Res. Vet. Sci. 132: 332-337.
TORRENTS, J.; MOREL, N.; ROSSNER, M.V.; MARTINEZ, N.C.; TOFFALETTI, J.R.; NAVA, S. 2020b. In vitro diagnosis of resistance of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus to fipronil in Argentina. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 82: 397-403.
ZAR, J.H. 1999. Biostatistical analysis. 4th ed., Prentice-Hall, Nueva Jersey, 663 p.







