Efecto del zinc orgánico en la producción y calidad de la carne de bovinos y ovinos en sistema de engorda intensiva
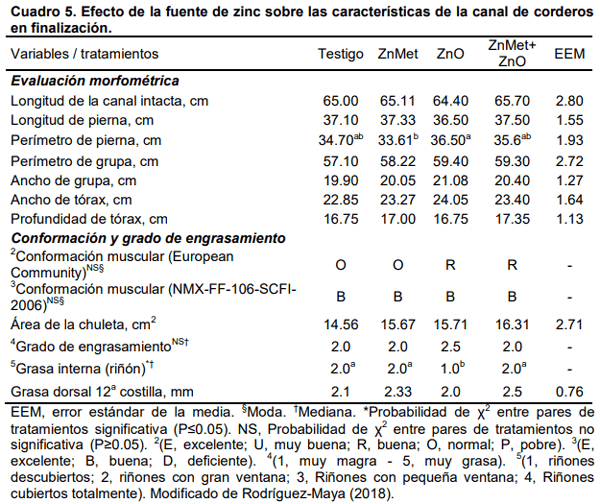
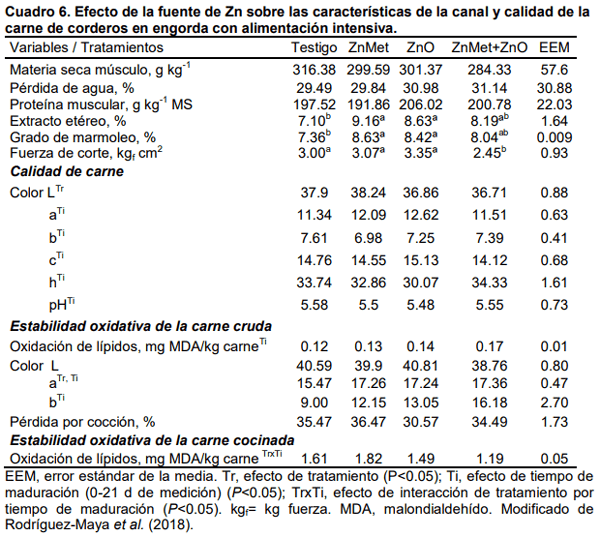
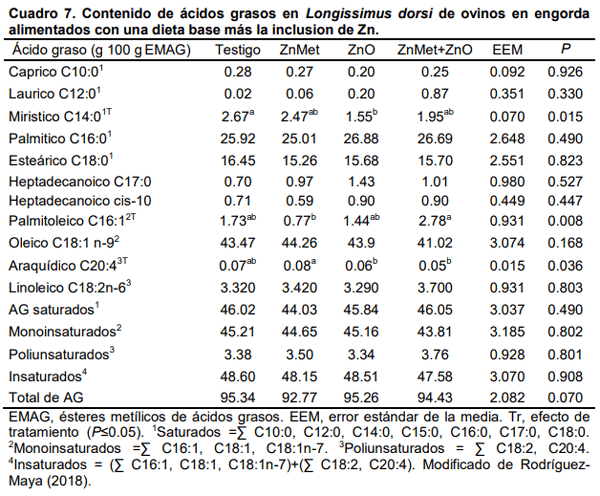
La suplementación de minerales en las dietas de ovinos ha permitido mejorar la salud, bienestar y nivel de producción. El zinc suplementario está asociado con mecanismos estimulantes de lipogénesis y reducción de lipólisis. En músculo la concentración molar del Zn2+ actúa en el metabolismo del transporte de la membrana y actúa como segundo mensajero en el citosol, además, es componente estructural de la insulina al promover la cristalización del polipéptido; de tal forma que, el zinc es fundamental en el metabolismo catalítico, estructural y de señalización celular en respuesta a la utilización de la energía; específicamente por la activación de transportadores ZIP y ZnT. La inclusión de Zn en dietas para rumiantes ha demostrado distintos efectos sobre la fuerza de corte, color de carne y pH muscular. En bovinos, el zinc mejora el rendimiento productivo y grado de marmoleo de la chuleta, así como la calidad de la canal; en gran medida por el aumento del depósito de grasa intramuscular y agregación de lípidos en la célula. La inclusión de Zn en la dieta al tener efecto lipogénico, puede afectar la expresión de ezimas del metabolismo lipídico del Longissimus dorsi. Por lo tanto, el objetivo del presente trabajo fue revisar los efectos del uso del Zn como aditivo incluido en la dieta sobre el rendimiento productivo, calidad de la carne y expresión génica en músculo de rumiantes alimentados en sistema intensivo.
Palabras clave: zinc, crecimiento, calidad de carne, bovinos, ovinos.
Aurousseau, B., Bauchart, D., Calichon, E., Micol, D., and Priolo, A. 2004. Effects of grass or concentrate feeding systems and rate of growth on triglycride and phospholipid and their fatty acids in the M. longissimus thoracis of lambs. Meat Sci. 66: 531-541.
Calnan, H.B., Jacob, R.H., Pethick, D.W., and Gardner, G.E. 2014. Factors affecting the colour of lamb meat from the longissimus muscle during display: The influence of muscle weight and muscle oxidative capacity. Meat Sci. 96: 1049-1057.
Chavey, C., Mari, B., Monthouel, M. N., Bonnafous, S., Anglard, P., Van Obberghen, E., and Tartare-Deckert, S. 2003. Matrix metalloproteinases are differentially expressed in adipose tissue during obesity and modulate adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 11888-11896.
Christensen, S., and Purslow, P.P. 2016. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in muscle and adipose tissue development and meat quality: A review. Meat Sci. 119: 138-146.
Coulston, L. and Dandona, P. 1980. Insulin-like effect of zinc on adipocytes. Diabetes 29: 665-667.
Essén-Gustavsson, B., Karlsson, A., Lundström, K., and Enfält, A.C. 1994. Intramuscular fat and muscle fibre lipid contents in halothane-gene-free pigs fed high or low protein diets and its relation to meat quality. Meat Sci. 38: 269-277.
Faustman C., Sun, Q., Mancini, R., and Suman, S.P. 2010. Myoglobin and lipid oxidation interactions: Mechanistic bases and control. Meat Sci. 86: 86-94.
Gallardo, M., Arias-Darraz, L., and Cárcamo, J. 2019. Effect of Breed on Transcriptional and Protein Expression of lipogenic enzymes in tail and subcutaneous adipose tissue from two grazing breeds of lambs. Animals. 9(64): 1-11.
Greene, L.W., Lunt, D.K., Byers, F.M., Chirase, N.K., Richmond, C.E., Knutson, R.E., and Schelling, G.T. 1988. Performance and carcass quality of steers supplemented with zinc oxide or zinc methionine. J. Anim. Sci. 66: 1818-1823.
Guerrero-Barcena. 2017. Efecto de la suplementación de clorhidrato de zilpaterol y zinc orgánico en la respuesta productiva, metabólica y calidad de la carne de ovinos en engorda intensiva. Tesis de Maestría. Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México. 95 p.
Huang, L., and Tepaamorndech, S. 2013. The SLC30 family of zinc transporters - a review of current understanding of their biological and pathophysiological roles. Mol. Aspects Med. 34: 548-560.
Huang, L., Tepaamorndech, S., Kirschke, C. P., Newman, J.W., Keyes, W.R., Pedersen, T.L., and Dum, J. 2018. Aberrant fatty acid metabolism in skeletal muscle contributes to insulin resistance in zinc transporter 7 (Znt7)-knockout mice. J. Biol. Chem. 293:7549- 7563.
Jeong, J., and Eide, D.J. 2013. The SLC39 family of zinc transporters. Mol. Aspects Med. 34: 612-619.
May, J.M. and Contoreggi, C.S. 1982. The mechanism of the insulin-like effects of ionic zinc. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 4362-4368.
Malcolm-Callis, K.J., Duff. G.C., Gunter, S.A, Kegley, E.B. and Vermeire, D.A. 2000. Effects of supplemental zinc concentration and source on performance, carcass characteristics, and serum values in finishing beef steers. J. Anim. Sci. 78: 2801- 2808.
McBeth, L. J., D. R. Stein, A. T. V. Pillai, M, J. Hersom, C. R. Krehbiel, U. De Silva, R. D. Geisert, J. R. Malayer, J. B. Morgan, C. K. Larson, and R. L. Ball. 2005. Effect of zinc source and level on finishing cattle performance, carcass characteristics, and adipocyte differentiation. Okla. Agr. Exp. Sta. Res. 4: 1-9.
Mortimer, S.I., van der Werf, J.H.J., Jacob, R.H., Hopkins, D.L., Pannier, L., Pearce, K.L., Gardner, G.E., Warner, R.D., Geesink, G.H., Hocking Edward, J.E., Ponnampalam, E.N., Ball, A.J., Gilmour, A.R., and Pethick, D.W. 2013. Genetic parameters for meat quality traits of Australian lamb meat. Meat Sci. 96: 1016-1024.
Myers, S.A., Nield, A., Chew, G.S., and Myers, M.A. 2013. The zinc transporter, Slc39a7 (Zip7) is implicated in glycaemic control in skeletal muscle cells. PLoS One 8: e79316. National Research Council. 1996. Nutrient requirements of beef cattle. 7th ed. National Academic Press, Washington, D.C.
Nunnery, G.A., Vasconcelos, J. T., Parsons, C. H., Salyer, G. B., Defoor, P. J., Valdez, F. R., and Galyean, M. L. 2007. Effects of source of supplemental zinc on performance and humoral immunity in beef heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 85: 2304-2313.
O’Grady, M.N., Monahan, F.J., Bailey, J., Allen, P., Buckley, D.J., and Keane, M.G. 1998. Colour-stabilising effect of muscle vitamin E in minced beef stored in high oxygen packs. Meat Sci. 50: 73-80.
Oh, Y.S. and Choi, C.B. 2004. Effects of zinc on lipogenesis of bovine intramuscular adipocytes. Asian-Australasian J. Anim. Sci. 17: 1378-1382.
Ohashi, k., Nagata, Y., Wada, E., Zammit, P.S., Shiozuka, M., and Matsuda, R. 2015. Zinc promotes proliferation and activation of myogenic cells via the P13K/Akt and ERK signaling cascade. Exp. Cell Res. 333: 228-237.
Park, K.S., N.G. Lee, K.H. Lee, J.T. Seo, K.Y. Choi. 2003. The ERK pathway involves positive and negative regulations of HT-29 colorectal cancer cell growth by extracellular zinc. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointes. Liver Physiol. 285: 1181-1188.
Paskavitz, A.L., Quintana, J., Cangussu, D., Taver-Montañez, C., Xiao, Y., Ortiz-Miranda, S., Navea, J.G. and Padilla-Benavides, T. 2018. Differential expression of zinc transporters accompanies the differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 49: 27-34.
Powell, S. 2000. The antioxidant properties of zinc. J. Nutr. 130: 1447S–1454S.
Purslow, P.P. 2005. Intramuscular connective tissue and its role in meat quality. Meat Sci. 70: 435-447.
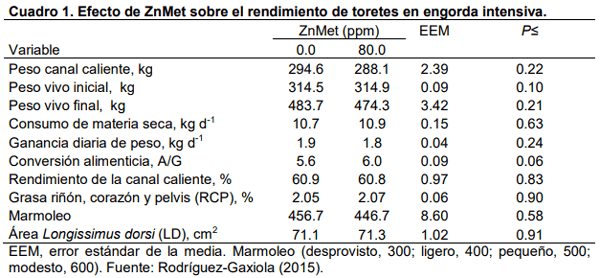
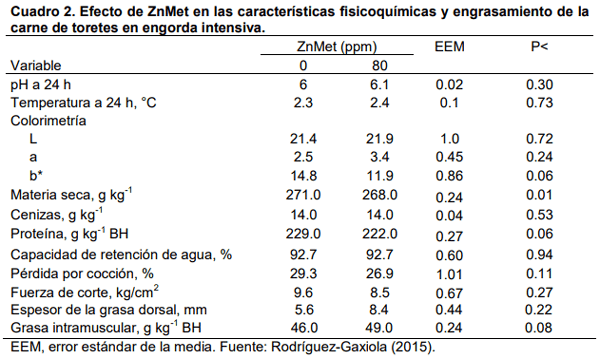
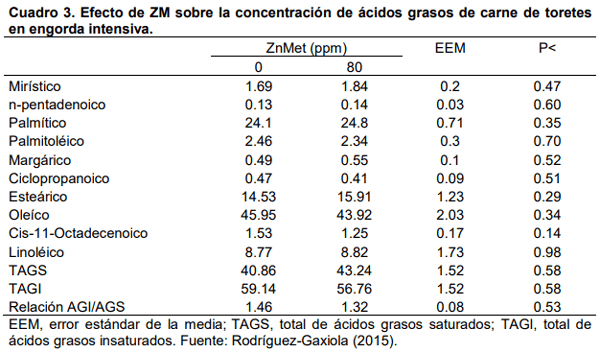
Rodríguez-Gaxiola, M.A. 2015. Efecto de la complementación dietaria del clorhidrato de zilpaterol y su interacción con zinc y cromo orgánicos en la respuesta productiva, características de la canal y calidad de la carne de bovinos y ovinos en engorda intensiva. Tesis de Doctorado en Ciencias Agropecuarias y Recursos Naturales. FMVZ-UAEMex. Toluca, México. 114 p.
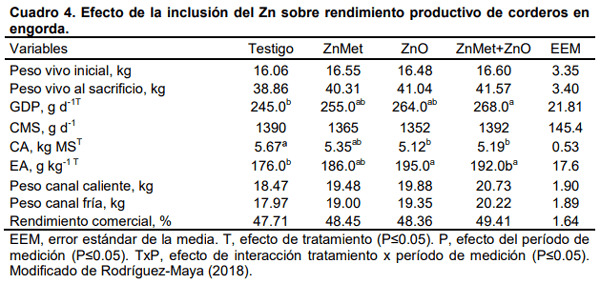
Rodríguez-Maya, M.A. 2018. Efecto del zinc orgánico (Zn-metionina) y zinc inorgánico (ZnO) en la respuesta productiva, características de la canal y calidad de carne de ovinos en engorda con alimentación intensiva. Tesis de Maestría en Ciencias Agropecuarias y Recursos Naturales. FMVZ-UAEMex. Toluca, México. 90 p.
Spears, J.W. and Kegley, E.B. 2002. Effect of zinc source (zinc oxide vs. zinc proteinate) and level on performance, carcass characteristics, and immune response of growing and finishing steers. J. Anim. Sci. 80: 2747-2752.
Thirumoorthy, N., Sunder, S.A., Kumar, M.K., Kumar, S.M., Ganesh, G., and Chatterjee, M. 2011. A review of metallothionein isoforms and their role in pathophysiology. World J. Surg. Oncol. 9: 54.
Zakrys, P.I., Hogan, S.A., O'Sullivan, M.G., Allen, P., and Kerry, J.P. 2008. Effects of oxygen concentration on the sensory evaluation and quality indicators of beef muscle packed under modified atmosphere. Meat Sci. 79: 648-655.







