Demostración inmunohistoquímica de Mycoplasma bovis en lesiones neumónicas crónicas en ganado en corral de engorda
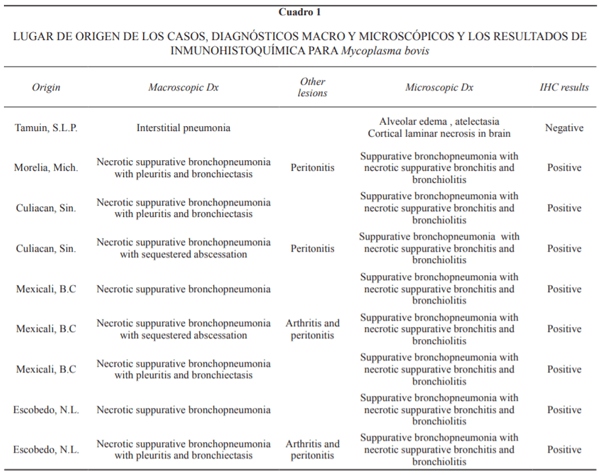
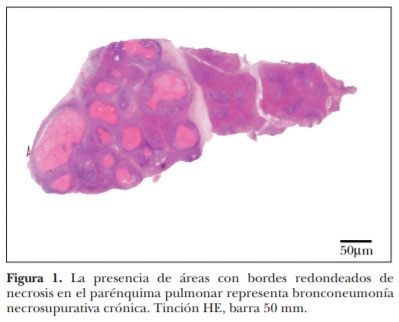
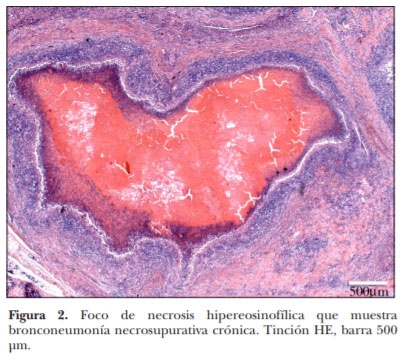
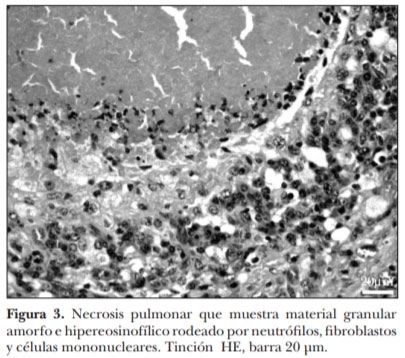
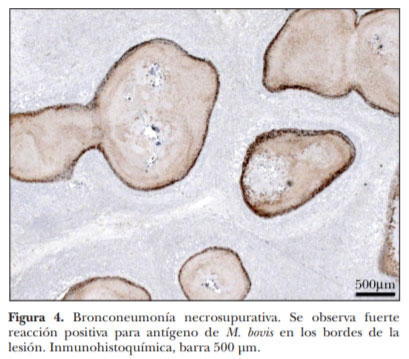
El corral de engorda es un sistema de producción intensivo de gran importancia en la ganadería de carne en México, Canadá y Estados Unidos de América. Estudios epidemiológicos indican que las enfermedades respiratorias de los bovinos son el principal problema en corrales de engorda. En este trabajo se describen las lesiones macroscópicas y microscópicas en pulmones de ganado de carne con severa neumonía crónica, a pesar de haber recibido tratamiento con antibióticos en más de tres ocasiones. Se realizaron estudios post mortem de ganado en corrales de engorda localizados en General Escobedo, Nuevo León; Morelia, Michoacán; Mexicali, Baja California y Culiacán, Sinaloa, todos en México. Se seleccionaron ocho casos crónicos de bronconeumonía supurativa con múltiples focos nodulares de exudado necróticocaseoso. Estos focos necróticos estaban microscópicamente centrados en bronquios y bronquiolos y sus bordes estaban claramente limitados por una reacción piogranulomatosa. Los estudios de inmunohistoquímica demostraron positividad a Mycoplasma bovis en todos los casos. Las lesiones neumónicas macro y microscópicas asociadas con M. bovis tienen un patrón conspicuo. Este es el primer informe de M. bovis en neumonías en ganado de corral de engorda en México.
Palabras clave: Mycoplasma bovis, NEUMONÍAS CRÓNICAS, GANADO EN CORRAL DE ENGORDA.
BANCOROFT JD, STEVENS A. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone, 1996.
ADEGBOYE DS, RASBERRY U, HALBUR PG, ANDREWS JJ, ROSENBUSCH RF. Monoclonal antibody-based immunohistochemical technique for the detection of Mycoplasma bovis in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded calf lung tissues. J Vet Diagn Invest 1995; 7:261-265.
ADEGBOYE DS, HALBUR PG, CAVANAUGH DL, WERDIN RE, CHRISTOPHER CL, CHASE CCL et al. Immunohistochemical and pathological study of Mycoplasma bovis-associated lung abscesses in calves. J Vet Diagn Invest 1995; 7:333-337.
KHODAKARAM-TAFTI A, LOPEZ A. Immunohistopathological findings in the lungs of calves naturally infected with Mycoplasma bovis. J Vet Med A 2004; 51:10-14.
BOOKER CW, ABUTARBUSH SM, MORLEY PS, KEE JIM G, PITTMAN TJ, SCHUNICHT OC et al. Microbiological and histopathological findings in cases of fatal bovine respiratory disease of feedlot cattle in western Canada. Can Vet J 2008; 49:473-481.
FULTON RW, BLOOD KS, PANCIERA RJ, PAYTON ME, RIDPATH JF, CONFER AW et al. Lung pathology and infectious agents in fatal feedlot pneumonias and relationship with mortality, disease onset, and treatments. J Vet Diagn Invest 2009; 21:464-477.
JARAMILLO-ARANGO CJ, TRIGO TAVERA FJ, SUÁREZ-GÜEMES F. Mannheimiosis bovina: etiología, prevención y control. Vet Méx 2009; 40:293-314.
CONFER AW. Update on bacterial pathogenesis in BRD. Anim Health Res Rev 2009; 10:145-148.
GRIFFIN D. Bovine pasteurellosis and other bacterial infections of the respiratory tract. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 2010; 26:57-71.
GAGEA MI, BATEMAN KG, VAN DREUMEL T, MCEWEN BJ, CARMAN S, ARCHAMBAULT M et al. Diseases and pathogens associated with mortality in Ontario beef feedlots. J Vet Diagn Invest 2006; 18:18-28.
GAGEA MI, BATEMAN KG, SHANAHAN RA, VAN DREUMEL T, MCEWEN BJ, CARMAN S et al. Naturally occurring Mycoplasma bovis-associated pneumonia and polyarthritis in feedlot beef calves. J Vet Diagn Invest 2006; 18:29-40.
KRYSAK DE. Chronic pneumonia and polyarthritis syndrome in a feedlot calf. Can Vet J 2006; 47:1019-1021. LAMM CG, MUNSON L, THURMOND MC, BARR BC, GEORGE LW. Mycoplasma otitis in California calves. J Vet Diagn Invest 2004; 16:397-402.
HAINES DM, MOLINE KM, SARGENT RA, CAMPBELL JR, MYERS DJ, DOIG PA. Immunohistochemical study of Hemophilus somnus, Mycoplasma bovis, Mannheimia hemolytica, and bovine viral diarrhea virus in death losses due to myocarditis in feedlot cattle. Can Vet J 2004; 45:231-234.
DYER N, HANSEN-LARDY L, KROGH D, SCHAAN L, SCHAMBER E. An outbreak of chronic pneumonia and polyarthritis syndrome caused by Mycoplasma bovis in feedlot bison (Bison bison). J Vet Diagn Invest 2008; 20:369-371.
DYER NW, KROGH DF, SCHAAN LP. Pulmonary mycoplasmosis in farmed white-tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J Wild Dis 2004; 40:366-370.
LOPEZ A. Respiratory System. In: MCGAVIN MD, ZACHARY JF, editors. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2007:463-558.
CORRIN B, NICHOLSON AG. Pathology of the Lungs, 2nd ed. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone, 2006.
INFANTE F, INFANTE FJR, FLORES-GUTIERREZ GH. Improved immunobinding test using monoclonal antibodies for detection of Mycoplasma bovis in milk. Can J Vet Res 2002; 66:282-284.
FLORES-GUTIERREZ GH, INFANTE F, SALINASMELENDEZ JA, THOMAS CB, ESTRADA-BELLMANN PC, BRIONES-EMCINIA F. Development of an immunobinding assay with monoclonal antibodies to diagnose Mycoplasma bovis in semen. Vet Res Comm 2004; 28:681-686.
JARAMILLO ML, AGUILAR RF, SALAS TE. Aislamiento de Mycoplasma bovis de neumonías de becerros. Memorias XIII Congreso Nacional de Buiatría, 1987; 328-331.
DELGADO GR. Neumonía y otitis en becerros Holstein asociadas a infección por Mycoplasms bovis. Memorias XIX Congreso Nacional de Patología Veterinaria, 2010: 306-315.
GOURLAY RN, HOUGHTON SB. Experimental pneumonia in conventionally reared and gnotobiotic calves by dual infection with Mycoplasma bovis and Pasteurella haemolytica. Res Vet Sci 1985; 38: 377-382.
SHAHRIAR FM, CLARK EG, JANZEN E, WEST K, WOBESER G. Coinfection with bovine viral diarrhea virus and Mycoplasma bovis in feedlot cattle with chronic pneumonia. Can Vet J 2002; 43:863-868.
JUÁREZ BARRANCO F, TRIGO TAVERA FJ, CHÁVEZ GRIS G, VARGAS GARCÍA R. Identificación de agentes virales por inmunohistoquímica en enfermedades respiratorias de bovinos en corral de engorda. Vet Méx 2003, 34:1-12.











